Back to Megiddo
A new expedition will explore the jewel in the crown of Canaan/Israel
026

028
Tel Megiddo is widely regarded as the most important archaeological site in Israel from Biblical times, and as one of the most significant sites for the study of the ancient Near East generally. It was inhabited continuously for more than five millennia, from about 6000 to around 500 B.C.E.
Megiddo’s military importance and long history as an international battleground is aptly reflected in the Apocalypse, the New Testament book of Revelation. Armageddon (a corruption of the Hebrew Har Megiddo—The Mount of Megiddo) is where, at the end of days, demons will gather the hosts of the nations for the ultimate battle against the forces of God (Revelation 16:16). At Megiddo, the day of the Lord will bring defeat upon the armies of darkness.
Strategically located, Megiddo controlled one of the most important military and trade routes of antiquity, the Via Maris, which linked Egypt in the south with Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia to the north and east. The mound overlooks the Via Maris as it emerges from a narrow pass in the Carmel ridge leading eastward into the Jezreel Valley. Megiddo also commands a beautiful view of the valley, with Mt. Tabor, Mt. Gilboa and Nazareth in the background to the east, and with the summit of Mt. Carmel visible to the north. The fertile Jezreel Valley, with its outlying villages, furnished the city’s economic base. Two springs at the foot of the mound, in the southwest and in the northeast, supplied water to Megiddo’s inhabitants.
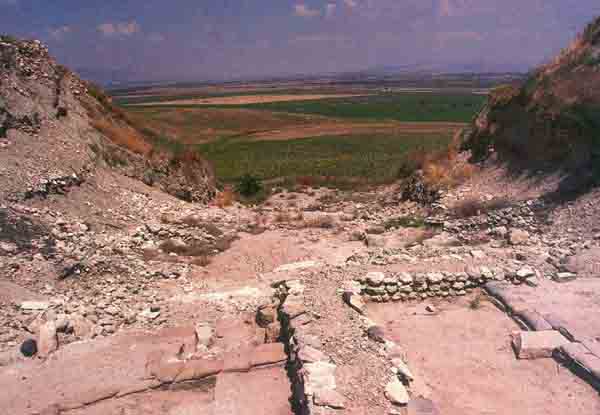


The site has been excavated three times since the beginning of the century. Ours will be the fourth. It is the richest site ever dug in Israel. The history of the Megiddo excavations is in many ways the history of Biblical archaeology, its methods and techniques.1
Though these past excavations have uncovered large parts of the mound, almost every level, every building and every historical interpretation has stirred fierce scholarly dispute. These controversies have not been resolved over the years, despite occasional new probes and re-examination of old excavation records. Because Megiddo is a cornerstone in the archaeology of Israel, the unresolved issues at the site are in many ways critical for the archaeological and historical study of the entire Levant.
For these reasons, the Institute of Archaeology of Tel Aviv University is launching a major, new, long-term excavation project at Tel Megiddo, directed by 029the authors. The renewed excavations will systematically uncover some of the still-unknown parts of the site and attempt to answer some of the unsolved puzzles remaining from previous excavations2
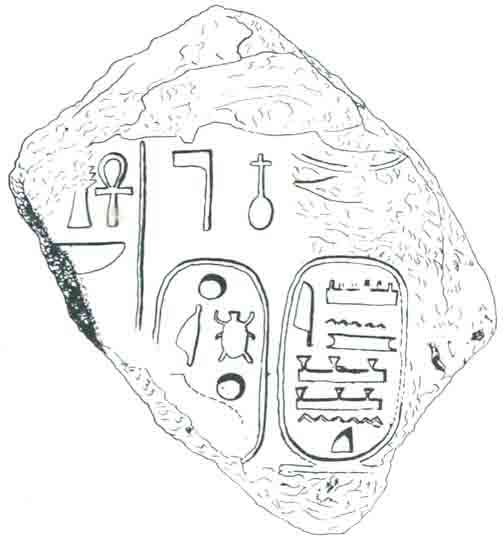
The first excavation of the site was undertaken between 1903 and 1905 on behalf of the German Society for the Study of Palestine by Gotlieb Schumacher, an engineer who lived in the German community of Haifa.3 Schumacher cut a 65-foot-wide trench across the mound from north to south and a number of smaller trenches in other parts of the site, identifying six building levels. His most famous find is a jasper seal portraying a roaring lion and inscribed “(belonging) to Shema, servant of Jeroboam.” Shema was apparently a high official of the king of the northern kingdom, either Jeroboam I (end of tenth century B.C.E.) or Jeroboam II (eighth century B.C.E.). This striking emblem of a powerful lion was sent by Schumacher to the Turkish Sultan in Constantinople, who kept it there in his royal collection. It is not clear what happened to it later, but today its whereabouts are unknown.

In 1925, excavation at Megiddo resumed under the auspices of the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago. Initiated by its famous director, Egyptologist James H. Breasted, it was led by Clarence Fisher, who was succeeded by P.L.O. Guy, who was succeeded by Gordon Loud. Large-scale work nevertheless continued until the outbreak of World War II in 1939.
With a generous grant from John D. Rockefeller, the Oriental Institute team operated on a grand scale, including the use of a balloon for aerial photography and the construction of their own beautiful expedition house complete with tennis courts. The 030expedition house now serves as offices for the Israel National Parks Authority.
The original goal of the Oriental Institute excavators was to “peel off,” one by one, each layer of habitation at the site, finally reaching bedrock. This was a critically defective methodology, on two counts. First, it was such a gargantuan task that it was impossible to complete, even with Rockefeller money behind it. When this became evident to the excavators, they abandoned the “peel-off strategy” and instead concentrated their efforts in selected areas. Second, exposing one layer at a time made it impossible for the excavators to assess the vertical relations that are essential to understanding the stratigraphy of the site. This serious methodological error accounts for much of the horrendous confusion that has characterized the interpretation of the site ever since.
Nevertheless, the Oriental Institute excavators did make a number of extraordinary discoveries and identified 20 major levels from the Neolithic period (sixth millennium B.C.E.) to the Persian period (fifth century B.C.E.).4
During the 1960s and early 1970s, Yigael Yadin returned to Megiddo for three short seasons on behalf of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. His objective was to clarify the complicated stratigraphic problems related to the remains of the Solomonic period (tenth 031century B.C.E.), in particular, the fortifications.5 In some respects he was successful, but in others he only added to the confusion.
The mound of Megiddo itself—a modest 15 acres—rises more than 100 feet above the broad expanse of the Jezreel Valley. At various periods Megiddo was enlarged to include a lower city northwest of the tell that doubled the area of the city. The steep slopes of the mound give an indication of the massive fortifications buried inside.
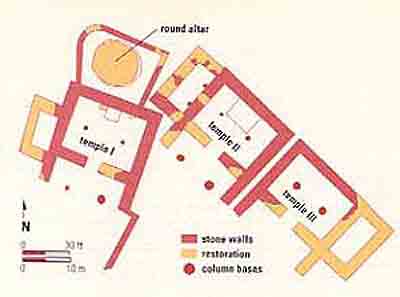
Excavations on the eastern slope of the mound revealed the earliest remains of late Neolithic (sixth to fifth millennium B.C.E.), Chalcolithic (fourth millennium B.C.E.) and Early Bronze (end of fourth to third millennium B.C.E.) settlements. The excavators uncovered a sacred area from as early as the Early Bronze Age with successive, superimposed temples that continued to function as a sacred area all the way into the beginning of the Iron Age. In the earliest temple, a unique ceremonial copper spear was found, perhaps belonging to some long-lost warrior-priest.
In the Early Bronze Age, this area became a magnificent ritual compound focusing on an immense circular stone structure—a bamah, or an altar—26 feet in diameter and 5 feet high, with seven steps leading up to the top. Nearby were three nearly identical temples, each consisting of a rectangular broadrooma with two support pillars near the center of the room and an altar on the back wall. Each temple was entered through a wide porch in front and was probably dedicated to a different deity. This impressive cultic compound can still be seen at the site. In some respects the circular stone structure probably resembles the later Biblical “high places” (for instance, 1 Samuel 9–10). High places like these were accepted as appropriate cult places during the period of the Judges (12th–11th centuries B.C.E.), but were eliminated during the religious reforms of Hezekiah and Josiah in the eighth and seventh centuries B.C.E.
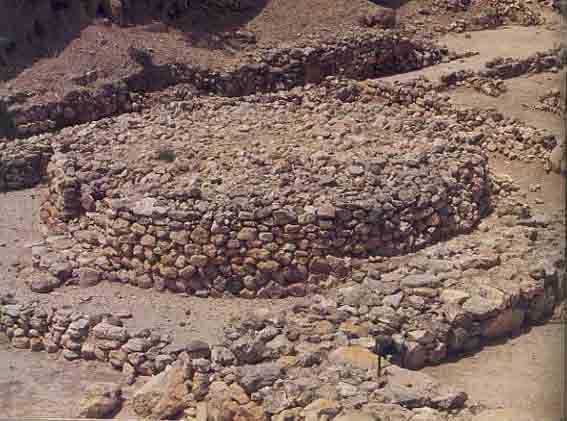

Another significant discovery from the Early Bronze Age is a massive wall—about 25 feet wide, preserved to a height of 13 feet—unearthed on the eastern slope. This is both the earliest and the strongest of many walls that protected the city over the millennia. However, the British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon (who excavated at Jericho and Jerusalem) had a different, quite plausible, interpretation of this Early Bronze wall: She argued that it was a retaining wall, built to support a large edifice higher up on the slope. Whether she is right is one of the questions we hope to answer in our excavation.
We can say with confidence that, in the Middle Bronze Age (starting in the beginning of the 20th century B.C.E.), the city was surrounded by a fortification wall and entered through an impressive city gate. A glacis (a steeply sloped earthen rampart) extended down from the base of the city wall. This is the beginning of the flourit of Canaanite Megiddo as a fortified urban center. The Canaanite city-state of Megiddo lasted throughout the Middle Bronze Age and the Late Bronze Age (for about 800 years), although at times it was clearly under Egyptian dominion and at other times was merely under Egyptian influence. Control of Megiddo was a prerequisite for Egyptian hegemony over Canaan.
Among the finds of the Middle Bronze Age was a broken black stone statuette of Thuthotep, a high Egyptian official of the 19th century B.C.E. Whether this reflects Egyptian dominance or simply influence is not clear.
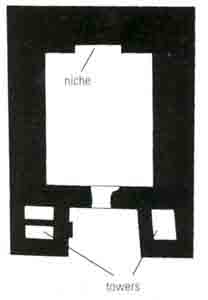
In the Middle Bronze Age city, the Early Bronze Age sacred area continued to be used, specifically the large circular structure and at least one of the adjacent temples. An additional temple (Temple 2048) replaced them later in this period. Two massive towers flanked the entrance to this temple, so, like a similar temple from the same period found at Shechem, it is referred to as a “tower temple” or a “fortress temple.” The latter designation stems from the fact that the walls of this temple were over 10 feet thick, which means that the walls probably extended to a considerable height. Temple 2048 consisted simply of a large rectangular building 70 feet long and over 50 feet wide, with a niche in the back wall of the temple room.
Also from this period was a large building with thick stone walls that Schumacher identified as a palace. Adjoining the palace was another stone building in which he excavated three unique stone tombs. One of them contained a skeleton lying on a bench, with a variety of gold adornments and gold-mounted scarabs. This could well have been the burial precinct of the royal dynasty of Canaanite Megiddo. The skeleton was probably a prince of Megiddo. Four more skeletons, probably of his family or entourage, and many burial presents were found on the floor.
The Late Bronze Age, beginning in about 1550 B.C.E., brings us to another kind of archaeological, as well as historical, problem. From an extraordinarily detailed Egyptian account—a hieroglyphic inscription incised on the walls of the Temple of Amun at Karnak, on the Nile in Upper Egypt—we know of the conquest of Megiddo by Pharaoh Thutmose III in 1479 B.C.E. This account fits perfectly with the geography and topography of the site, lending a dramatic reality to one of history’s great battles. But the archaeology of the site presents problems—and not only for Megiddo.
According to the Egyptian account, Thutmose III marched north with his army to reestablish Egyptian domination in Canaan. A confederation of Canaanite cities, led by the king of Kadesh (on the Orontes River in Syria) prepared to meet him at Megiddo—strategically, the most advantageous place from their Canaanite viewpoint. Thutmose and his commanders considered which of three alternative routes to take to 032cross the chain of hills separating Megiddo from the coastal plain—the main road going directly to Megiddo or one of two alternate routes to the north and to the south. The main road ends in the narrow Qina pass (the northeastern end of modern Nahal Iron, Wadi ‘Ara in Arabic) that opens into the Jezreel Valley near Megiddo. The Egyptian commanders, fearful that the Canaanite army would ambush them on the direct but narrow road, urged the pharaoh to take either the northern or the southern route. Thutmose rejected their advice, however, and made a daring tactical decision. Assuming that the Canaanite leaders would think like his generals and await him near Taanach on the southern alternate or Yoqneam on the northern alternate (and probably both), he decided to take his army through the perilous Nahal Iron. He was right. The Egyptian army passed through unmolested and routed the Canaanite chariotry in open battle near Megiddo.
The deliberations of Thutmose and his generals, preserved in the Egyptian annals, vividly capture the intensity of this debate 3,500 years ago.
The victorious Egyptians seized rich booty, including hundreds of chariots. But instead of immediately proceeding to capture the city, the Egyptians simply enjoyed looting the equipment the Canaanites left on the field of battle. Meanwhile, the Canaanites managed to reach the city and reorganize. Thutmose had to lay siege to the city and only after seven months was he able to capture it. Again, according to the Egyptian records, the Egyptian army looted the conquered Canaanites (the list of booty is long and detailed) and Canaan became a province in the Egyptian empire. The Egyptian governor of Canaan may have resided at Megiddo.
Oddly enough, no remains of a destruction of Megiddo at this time have been uncovered in any of the excavations. Perhaps the city finally surrendered, thereby avoiding destruction.
But this is not the only archaeological mystery. No evidence of a Late Bronze Age city wall has been discovered. This is true not only at Megiddo, but at other important sites like Hazor, Shechem and Lachish. Huge fortifications, characterized by a massive city wall and a huge rampart or glacis, are typical of Middle Bronze Age urban centers. But, at least from the archaeological evidence, these same Late Bronze Age cities were unfortified.
How could Thutmose lay siege to an unfortified city for seven months?
Three possible solutions have been suggested:
(1) The earlier, massive Middle Bronze Age fortifications continued to function in the Late Bronze Age. (2) The Late Bronze Age city was protected by a belt of houses built along the upper periphery of the site; such houses, adjoining one another, could have formed a kind of a defense system around the city. (3) Megiddo was indeed unfortified, as recently suggested 033by Rivka Gonen, who interprets the story of Thutmose’s siege on that basis. According to this interpretation, the Egyptian army did not storm the walls or break through them, but instead laid a prolonged seige, surrounding the city with a girdle wall, and patiently waited for the city to surrender.
The only way to try to solve the problem of the Late Bronze Age fortifications at Megiddo is to renew excavations with up-to-date methodology. We will open new excavation fields and study afresh the stratigraphy of the old excavations. What we learn at Megiddo will help illuminate the other Late Bronze Age Canaanite sites as well.
In any event, after Thutmose’s victory the palace in the northern part of the site was extended, perhaps to accomodate the Egyptian governor. Its walls are approximately six feet thick and enclose a large courtyard in the center of the palace. The palace even contained a sizeable bathroom with a toilet-seat-like basin in its center and a floor covered with seashells set in lime plaster.
One very unusual find can also be dated to the Late Bronze Age. However, it was not excavated; it was found by a shepherd of Kibbutz Megiddo after the Oriental Institute excavators had closed shop. In a dump of excavated soil, the shepherd found a broken tablet, inscribed in cuneiform, bearing (on both sides) 37 lines of writing that included a portion of the Mesopotamian Epic of Gilgamesh. The full version of this epic, which deals with the unsuccessful quest of the hero for immortality, includes an episode strikingly similar to the flood story in the Bible.b We can date this copy to the Late Bronze Age by means of paleography, that is, the similarity to the sign forms of the Amarna tablets. It probably comes from a scribal school at Megiddo. This provides a tantalizing hint that there may be an archive of cuneiform tablets buried somewhere at Megiddo. Such an archive has never been found in Israel.

Another hint that there may be an archive at Megiddo comes from the el-Amarna letters, a 14th-century B.C.E. archive of 336 tablets discovered in 1887 and years following at el-Amarna on the eastern bank of the Nile, 185 miles south of Cairo. Among the cuneiform tablets were six letters sent by Biridiya, king of Megiddo, to the Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep III, or to his son Akhenaten (Amenhotep IV). One of them (No. 244) describes a threat to Megiddo from Labayu, the ruler of the powerful hill-country city-state of Shechem. Biridiya pleads with his Egyptian patron to send arms:
“To the king, my lord, and my Sun-god, say: Thus Biridiya, the faithful servant of the king. At the two feet of the king, my lord, and my Sun-god, seven and seven times I fall. Let the king know that ever since the archers returned [to Egypt], Labayu has carried on hostilities against me, and we are not able to pluck the wool, and we are not able to go outside the gate in the presence of Labayu, since he learned that thou hast not given archers; and now his face is set to take Megiddo, but let the king protect the city, lest Labayu seize it. Verily, there is no other purpose in Labayu. He seeks to destroy Megiddo.”
Unfortunately, we don’t have the other side of the correspondence. Perhaps we will find it when we go back to Megiddo.
The Amarna correspondence is only one piece—albeit a very large one—of evidence that Megiddo was a major player on the international stage in the Late Bronze period (1550–1200 B.C.E.), the period just before the emergence of Israel. A letter found at Hattusha, the Hittite capital on the Anatolian plateau (modern-day Turkey), also mentions Megiddo, as do other Egyptian texts, including the geographical description of Canaan known as Papyrus Anastasi I, dated to the 13th century B.C.E., during the reign of Ramesses II.
The most vivid testimony to Megiddo’s wealth and 036power at this time, as well as to its varied cultural contacts, is a hoard of magnificent ivories found in the Late Bronze Age palace. The hoard includes an ivory pen case with the cartouche of Ramesses III (1182–1151 B.C.E., according to the low chronology). So the hoard must have been added to as late as the mid-12th century. In the highlands, 1200 B.C.E. is usually taken to mark the beginning of the Iron Age. In the lowlands, however, it actually started 50 or 75 years later and the Late Bronze Age extended longer; so the mid-12th century at Megiddo would still be in the Late Bronze Age. This ivory hoard, despite the fact that it must have been placed here in the mid-12th century, still reflects the prosperity and cultural diversity of Late Bronze Age Megiddo as a major Canaanite city. Equally important, many scholars believe that these ivories were produced over a long period of time, going back to much earlier in the Late Bronze Age. The hoard consists of 382 objects portraying Egyptian, Hittite, Aegean and Assyrian influence. It is one of the richest assemblages of ancient ivories ever discovered.c
Megiddo enters the Biblical narrative in the time of the Judges (generally dated to the 12th–11th centuries B.C.E.). The prophetess Deborah enlisted Barak to lead the forces of Israel against the Canaanite forces of King Jabin of Hazor, commanded by Sisera (Judges 4). When the Canaanite army under Sisera was camped in the Nahal Kishon area, Barak charged down Mt. Tabor, throwing the Canaanite army into a panic. Sisera fled to the tent of Jael, wife of Heber the Kenite. Feigning friendship, Jael welcomed Sisera to her tent, but while he slept, she drove a tent peg through his forehead; when the Israelite commander Barak came in pursuit of his enemy, he found Sisera already dead.
Following the prose account in Judges 4 is the triumphant poem called the Song of Deborah in Judges 5. The scene of the battle is there described: “Then the kings came, they fought: / The kings of Canaan fought / At Taanach, by Megiddo’s waters— / They got no spoil of silver. / The stars fought from heaven, / From their courses they fought against Sisera. / The torrent Kishon swept them away, / The raging torrent, the torrent Kishon” (Judges 5:19–21).
Surprisingly enough, Megiddo is mentioned in the Bible both in the list of the cities conquered by Joshua (Joshua 12:21) and in the list of Canaanite cities not conquered by the settling Israelites (Judges 1:27–28).
While we do not know how Megiddo finally fell into Israelite hands, by King Solomon’s time, in the tenth century B.C.E., Megiddo had become the seat of one of his royal provinces (the 5th district);d Baana, son of Ahilud, served as district governor, residing at Megiddo (1 Kings 4:12). From the Bible we also know that Solomon left his stamp on Megiddo’s architecture:
“This was the purpose of the forced labor that King Solomon imposed: It was to build the House of the Lord, his own palace, the Millo and the wall of Jerusalem and Hazor and Megiddo and Gezer” (1 Kings 9:15).
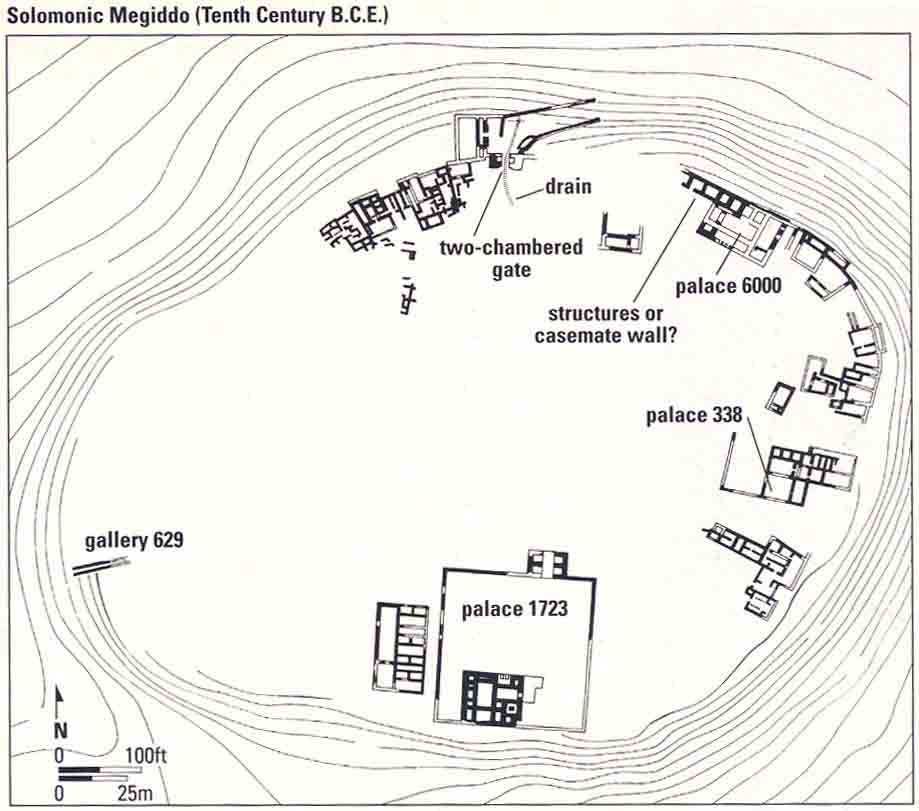
The grandeur of Solomon’s Megiddo is clearly evident in the archaeological finds at Megiddo—in large palaces, with fine, smooth-faced ashlar masonry and in elaborate decorative stonework.
Two or three different palaces were built on the south, north and east areas of the mound (marked 1723, 6000 and 3386 on the plan of Solomonic Megiddo in the tenth century B.C.E.), their facades facing the center and their back walls at the edge of the mound. The back walls of these palaces, with the addition of the walls of other domestic structures on the outer edge of the mound, formed a complete defense circle around the city.
Ashlar masonry was used lavishly in the construction of the palatial buildings of Solomonic Megiddo. Phoenician building techniques, brought by craftsmen sent to Solomon by his ally, King Hiram of Tyre, characterized Solomon’s building activities. Similar to Jerusalem, the ashlar walls of the buildings, “from foundations to coping and all the way out to the great courtyard, were of choice stones, hewn according to measure, smooth on all sides” (1 Kings 7:9).
Proto-Ionic capitals from Solomonic Megiddo were found in various parts of the site. They were mounted 037on stone pilasters (columns attached to walls) and on freestanding columns, which no doubt decorated monumental entrances to the buildings.

A major disagreement concerns the city gate of Solomon’s Megiddo. In the description of Solomon’s building activities in the Bible (1 Kings 9:15), Hazor, Gezer and Megiddo are mentioned together. At the first two sites, nearly identical six-chambered city gates (three chambers on each side that may have functioned as guardrooms or, in the case of the outer one, as the first story of a tower) were uncovered. The Hazor gate was excavated by Yadin. The one at Gezer was identified by Yadin by some clever detective work in the report of an early excavator of Gezer. Yadin was convinced that an almost identical six-chambered gate at Megiddo—assigned by its excavator P.L.O. Guy to King Solomon’s time—had indeed been built by the king’s architects, despite the many stratigraphical difficulties in this conclusion. In addition, Yadin thought he had uncovered what he considered to be a typical Solomonic casemate wall belonging to the Solomonic fortification system at Megiddo, consisting of two parallel walls with intermittent cross-walls that create rooms called casemates. Yadin concluded that this “casemate wall” was connected to the “Solomonic gate” because casemates were already known from strata he identified as Solomonic at Gezer and Hazor. Our view is that Yadin erred in this interpretation of the stratigraphy. We do not believe that a casemate wall at Megiddo has been confirmed. Moreover, we believe that the Solomonic gate of Megiddo is a two-chambered gate below the six-chambered gate. This gives some idea of the kinds of problems that are involved in the stratigraphy of Megiddo.


We do not disagree with all of Yadin’s work at Megiddo, however. Perhaps the most important result 039of his work was the redating of “Solomon’s Stables,” the most famous archaeological structures at the site. The appellation Solomon’s Stables was given to two sets of structures on the northeast and southwest part of the mound by P.L.O. Guy. In 1 Kings 9:19, we are told that Solomon built “cities for chariots and cities for horsemen.” Guy concluded that these two sets of buildings were the stables Solomon built at Megiddo. Each of the two sets of structures consisted of a series of buildings with common walls between them. Each individual building consisted of three rooms (therefore called tripartite buildings) with rows of pillars dividing the side rooms from the center room. Between the pillars were stone ashlar blocks, scooped out as a basin that the excavators identified as mangers from which horses were fed. Many of the 040pillars had holes cut through them, which the excavators identified as holes for the ropes that tethered the horses. The center aisles appear to have been paved with lime plaster. The side rooms were paved with stone cobbling—so the horses would have a secure footing, according to the excavators.
The northern group of buildings consisted of 12 tripartite buildings of unequal size; the southern group, of five buildings of equal size. The southern complex opens onto a spacious, square courtyard with an installation in the center that the excavators said was a water basin for the horses.
Whether these tripartite buildings were stables is a hotly debated issue.e Many leading scholars—Yadin, John Holladay, Gabriel Barkay (and David Ussishkin)—defend the identification of these buildings as stables. Other leading scholars—James Pritchard, Yohanan Aharoni, Ze’ev Herzog, Anson Rainey, Larry Herr, Volkmar Fritz, John Currid—disagree. On the basis of similarity to pillared buildings excavated in other sites, such as Beer-Sheva, they identify them as storehouses or perhaps markets or even barracks for troops.
But on one thing, most of them agree. They do not date to King Solomon’s time. The Solomonic dating of the Oriental Institute excavators is demonstrably wrong, as Yadin’s soundings have shown. Whether stables or something else, these buildings date to the ninth century B.C.E., to the time of King Omri and King Ahab or possibly even later. Whether King Solomon had a horse stable at Megiddo is an intriguing question discussed by Graham Davies, beginning on page 44.
The reader will have noticed that we skipped from the end of the Late Bronze Age to Solomonic Megiddo, a gap of about 200 years. This was intentional. The stratigraphy of the intervening levels and their historic interpretation is not easy, and untangling it will be one of the most important aims of our new excavation.
In describing the excavation results thus far, we have not used strata numbers, but they will be helpful as we explore this nearly 200-year gap. The strata to be discussed were subdivided by the Oriental Institute excavators into As and Bs (B being earlier in time and lower than A), because in some areas there were separate phases to a single numbered stratum.
The last level we described before Solomonic Megiddo was where the ivory hoard was found, the latest additions to which dated to the time of Ramesses III (first half of the 12th century B.C.E.). This would normally place the stratum in which the ivory hoard was found in the archaeological period we call Iron Age I; however, this level was clearly culturally continuous with the previous level dating to the Late Bronze Age. These two levels have been labeled Stratum VIIB (the earlier one) and VIIA (the more recent one). They are separated by a destruction level, but no change in culture or city plan. The later level is the same prosperous Canaanite city as was found in Stratum VIIB. We cannot account for this destruction—who did it and why? This reminds us that not all destructions can be accounted for in the historical records available to us.
We might be tempted to ascribe this destruction to the Israelites—the time period seems to be right—but subsequent levels make this identification impossible. Moreover, a prosperous VIIA community just like the previous VIIB community also rules out the Israelites. Incidentally, the Bible gives no indication that Megiddo was conquered by the Israelites at this early period.
On top of Stratum VIIA is an enormous destruction level. The debris was sometimes as much as 4 feet deep. The next later level has been labeled VIB.
Stratum VIB at Megiddo appears to have been an unwalled settlement with poorly constructed buildings, representing a radical change in the layout of the city. This may indicate that a new and different group now inhabited the site. But who?
At about this time, two important demographic 041changes were occurring in Canaan: The Philistines—a people from the western Mediterranean—settled in the southern coastal plain of Canaan. Second, groups of people who would soon become the Israelites settled in the hill country to the south of Megiddo. Dozens of Iron Age I sites reflecting this new development have been recorded in the Jezreel Valley.
Should the destruction level on top of Stratum VIIA be assigned to the Israelites? To the Philistines? As we shall see, the latter is a possibility, but not the former.
In Stratum VIA, we again see a major change. Stratum VIA is completely different from Stratum VIB. In Stratum VIA dense residential structures were built of mudbrick on stone foundations (socles). Once again, as in the Late Bronze Age, we have a well-developed city. It is difficult to provide an historical explanation for this change. Then Stratum VIA was violently destroyed.
One of the candidates for the conqueror of Megiddo at the end of Stratum VIIA is the Philistines, as noted above. As Amihai Mazar has shown, the first 042Philistine pottery appears in the next later stratum, Stratum VI. Both phases of Stratum VI may have been a Canaanite-Philistine city, as scholars like Albrecht Alt, Benjamin Mazar and Yigael Yadin have suggested.

The destruction of Stratum VIA can then be attributed to King David. This is consistent with the fact that the next layer, Stratum VB is again a rather poorly built settlement, an appropriate candidate for King David’s Megiddo.
Yohanan Aharoni argued, on the other hand, that the Israelites rather than the Philistines were the conquerors of Stratum VIIA. The rich and varied ceramic assemblage from the Stratum VIA city included not only some decorated Philistine sherds but a group of collared-rim storage jars, once believed to indicate Israelite presence. However, few if any scholars would defend this position today.
In any event, Stratum VB is followed by Stratum VA–IVB, which, almost everyone now agrees, is the Solomonic city. It was William F. Albright who, more than 50 years ago, observed that Strata VA and IVB were in fact contemporaneous and belonged to one city level. There are still problems in deciding what to attribute to Stratum VA–IVB, but there is general agreement that whatever is found in that stratum is part of Solomonic Megiddo. This is important because in solving the problems of the stratigraphy of earlier periods, we must work back from Solomonic Megiddo as well as forward from Late Bronze Age Megiddo (Stratum VII).
These are the kinds of issues we hope to resolve by using modern methods, combined with a reevaluation of survey data in the Jezreel Valley.
The end of Stratum VA–IVB, King Solomon’s Megiddo, is not clear. After Solomon’s death the kingdom split apart, the north seceding from the south. Solomon’s son Rehoboam became king of Judah, the southern kingdom, and Jeroboam, son of Nabat, became king of Israel, the northern kingdom. Then, “in the fifth year of King Rehoboam, King Shishak of Egypt marched against Jerusalem and carried off the treasures of the house of the Lord and the treasures of the royal palace” (1 Kings 14:25–26). Shishak then turned north with his armies into the kingdom of Israel. Did he destroy Stratum VA–IVB at Megiddo?
Stratum VA–IVB was not completely destroyed. Only one palace (Palace 6000) and a few other buildings were leveled by fire. Perhaps this was caused by conflicts during the breakup of the kingdom or by later events, rather than by Shishak.
On the other hand, an Egyptian inscription lists Megiddo as one of the cities conquered in about 925 B.C.E. by Shishak (spelled Sheshonq in Egyptian 043records). A fragment of a stone-carved stele of Pharaoh Shishak was also uncovered at Megiddo. More than 10 feet high when it was complete, this stele was probably erected following Shishak’s victorious campaign. This does not necessarily mean that Shishak was responsible for the city’s destruction: Why would he have erected such a stele in a destroyed city? Probably the stele represents his conquest of the city and the destruction could have occurred sometime afterward.
The Megiddo of Stratum IVA radically differs from the Solomonic city. This later city became a fortified stronghold instead of a civilian district center, as it had been in Solomon’s time. It is to this city that the famed stables belonged, if they are indeed stables.
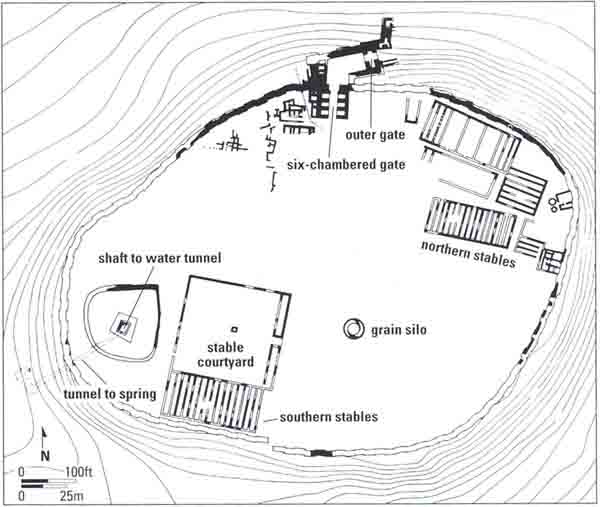
Interestingly, no residential quarters were discovered in this level. Megiddo was apparently a garrison city. A massive solid offset-inset wall, 12 feet wide, surrounded the city. The entrance into the city was probably through the six-chambered gateway. Its foundations were constructed with ashlars removed from the Solomonic (Stratum VA–IVB) buildings, but stratigraphically it must be dated to Stratum IVA, rather than earlier.


At the same time, an elaborate new water system was built to enable a safe approach to the spring located at the bottom of the southwestern slope of the mound. In the Solomonic period (Stratum VA–IVB) the southwestern spring, outside the city, was reached through an impressive gallery (gallery 629) that passed through the city wall by a postern gate. In the succeeding period, this exposed, and therefore vulnerable, access was changed. A square vertical shaft, about 115 feet deep, with stairs along its sides, was dug from the surface of the mound through the accumulation of earlier debris and into the bedrock. This square shaft then connected to a horizontal tunnel about 210 feet long, cut in the bedrock and leading to the spring that flowed more than 100 feet below the surface of the mound. At a later stage the tunnel was deepened, so that the grade of the tunnel enabled the spring water to flow to the vertical shaft.
By the last third of the eighth century B.C.E., expansion of the Assyrian empire reached the kingdom of Israel. In 734–732 B.C.E. Tiglath Pileser III, king of Assyria, led campaigns in Philistia and in the north of Israel. He annexed northern Israel, and Megiddo became the capital of the Assyrian province named Magiddu, which included both Megiddo and the Jezreel Valley. Stratum III at Megiddo probably dates to this period.
Two elaborate public buildings from this period display features of a typical Assyrian administrative center, notably a central, rectangular courtyard surrounded on all sides by halls and rooms. The buildings are located just where we would expect them, near the city gate. Several large blocks of houses separated by a grid of evenly spaced parallel streets intersecting at right angles were also uncovered. Here we have the entire Assyrian administrative center of Megiddo because Stratum III was excavated over the entire site, before the Oriental Institute excavators abandoned the strategy of “peeling off” the site straum by stratum.

The next stratum, Stratum II, dates to the seventh century B.C.E. In 609 B.C.E. Pharaoh Necho of Egypt crossed through the country on his way to Carchemish on the Euphrates; he wanted to help the Assyrians, who at the time were threatened by the Babylonians. According to the Bible, King Josiah of Judah marched toward Necho, but when he confronted him at Megiddo, Necho slew him. Josiah’s servants conveyed his body in a chariot from Megiddo to Jerusalem, and they buried him in his tomb (2 Kings 23:29–30). In the parallel account in Chronicles, Necho sends messengers to Josiah to tell him that he should not “march against” him, that the Egyptian ruler simply wants to pass through on his way to Carchemish. But Josiah did not accept this advice and in the end “came to fight [Necho] in the plain of Megiddo,” where Josiah was killed by an Egyptian arrow (2 Chronicles 35:20–24). Several interpretations of this event have been put forward by scholars, including the possibility (suggested by Nadav Na’aman) that Josiah came to Megiddo to pay homage to Necho, not to oppose him, and that Josiah was slain there, possibly over political disagreements. Avraham Malamat associates a fortress in this stratum with Necho’s campaign. Whether our excavations will clarify these matters is uncertain.
Stratum I was the last, dull, settlement on the mound—dating to the Babylonian and Persian periods. Megiddo then disappeared from history, ending more than 2000 years of service as the great guardian of the Nahal Iron entrance to the Jezreel Valley on the Via Maris.
For information about joining the excavation at Megiddo, see its listing in “1994 Excavation Opportunities.”
Tel Megiddo is widely regarded as the most important archaeological site in Israel from Biblical times, and as one of the most significant sites for the study of the ancient Near East generally. It was inhabited continuously for more than five millennia, from about 6000 to around 500 B.C.E. Megiddo’s military importance and long history as an international battleground is aptly reflected in the Apocalypse, the New Testament book of Revelation. Armageddon (a corruption of the Hebrew Har Megiddo—The Mount of Megiddo) is where, at the end of days, demons will gather the hosts of the nations for […]
You have already read your free article for this month. Please join the BAS Library or become an All Access member of BAS to gain full access to this article and so much more.
Already a library member? Log in here.
Institution user? Log in with your IP address or Username
Footnotes
Tikva Frymer-Kensky, “What the Babylonian Stories Can and Cannot Teach Us About the Genesis Flood,” BAR 04:04.
See Hershel Shanks, “Ancient Ivory—The Story of Wealth, Decadence and Beauty,” BAR 11:05.
Solomon divided the country into 12 districts The boundaries of some of them did not follow old tribal lines, an apparent effort to break down old tribal loyalties.
See Yigael Yadin, “In Defense of the Stables at Megiddo,” BAR 02:03; “Megiddo Stables or Storehouses?” BAR 02:03; John D. Currid, “Puzzling Public Buildings,” BAR 18:01.
Endnotes
For summaries of the results of past excavations, see G.I. Davies, Megiddo (Cambridge, 1986) and Aharon Kempinsky Megiddo: A City State and Royal Centre in North Israel (Munich, 1989).
The project is sponsored by the Israel Exploration Society and by the Israel Parks Authority, which maintains the site as a national park. Pennsylvania State University will take part in the expedition as a leading American sponsor and will be represented by Prof. Baruch Halpern, principal investigator and North American coordinator of the project. The project is funded by Earthwatch and its research corps. Other American, European and Israeli institutions will participate in the excavation consortium. The expedition will run an educational project for overseas students.
G. Schumacher, Tell el-Mutesellim 1 (Leipzig, 1908); C. Watzinger, Tell el-Mutesellim 2 (Leipzig, 1929).
For the final publication of the results, see the following titles by Oriental Institute Publications: R.S. Lamon, The Megiddo Water System (1935); H.G. May, Material Remains of the Megiddo Cult (1935); P.L.O. Guy, Megiddo Tombs (1938); R. Lamon and G.M. Shipton, Megiddo I (1939); G. Loud, The Megiddo Ivories (1939); G. Loud, Megiddo II. Seasons of 1935–1939 (1948).